
When you’re living with diabetes, physical activity and eating healthy are the two pillars that hold your life together. Besides other benefits, a diabetes diet, along with other lifestyle changes, can make managing the condition almost effortless. Why? Because what you eat and how much you eat can go a long way in keeping your blood sugar in check!
What is the benefit of eating healthy with diabetes?
Food has the biggest impact on glucose levels. When you have diabetes and eat healthily, it prevents blood sugar from fluctuating uncontrollably, making a huge difference to your health and keeping any complications at bay. And when your glucose is within the right range, your blood pressure and cholesterol remain so, too.
Moreover, a wholesome type 1 or type 2 diabetes diet helps you feel good, lose weight, have more energy, and delay any serious health problems. And, before you moan, eating healthily does not preclude you from enjoying your favourite foods. You can still have them, just less frequently and in smaller portions.
What foods should you eat if you have diabetes?
Diabetes is different for each person. Therefore, there are no specific guidelines on portion sizes. The correct diet for you may not be right for another person, which is why your doctor or health care provider is the best person to create your diabetes diet plan.
However, there are foods that you should (or should not) eat when living with diabetes. These need to be low in calories, trans fat, sugar, and salt.
1. Choose healthier carbs, especially if you take insulin. Instead of cold drinks, pasta, bread, and chips opt for carbohydrates that have a high amount of fibre, like sweet potatoes or beans.
2. Eat healthier fats, which means instead of butter or ghee, choose oils like olive, sunflower, or canola. Rather than bingeing on biscuits, cakes, and pastries, try nuts, fruits, seeds, and avocados. Fish like tuna and salmon are another good source of healthy fats.
The Diabetes Diet Food List | |
Vegetables | No starch: broccoli, carrots, greens, peppers, and tomatoes With starch: potatoes, corn, and green peas |
Fruits | Oranges, melon, berries, apples, bananas, and grapes |
Grains | Half the grains in a day have to be whole grains Brown rice, buckwheat, wheat, oats, cornmeal, barley, and quinoa |
Protein | Lean meat, tofu, fish, eggs, nuts, dried beans, chickpeas and split peas, chicken or turkey without the skin |
Dairy | Has to be non-fat or low-fat milk, yoghurt, and cheese |
What not to eat with diabetes?
As we said, foods brimming with saturated or trans-fat should not make it to your plate. Similarly, avoid anything filled with sodium. If you’re diabetic and have high blood pressure, then your sodium intake has to be less than 2,300 milligrams per day.
Eat fewer items with added sugar. This includes candies, ice cream, soda, juices, baked goods, energy drinks, etc. In case your day is incomplete without coffee or tea, use a sugar substitute in it. When you crave a sweetened beverage, chug water. You’ll not only cut calories but also avoid sugar highs and lows.
Limit your alcoholic beverages. Alcohol reduces glucose levels, especially for people who take diabetes medicine or are on insulin. Stick to one drink a day and always eat something while drinking.
How to manage blood sugar levels while eating healthy?
Keeping a check on what you eat is the starting point of managing diabetes. But there’s much more you can do.
• Never skip a meal, and if possible, eat at regular intervals.
• Use an app to track what you eat, drink, and your physical activity for the day.
• Keep control of your portions using either the plate method or carb counting.
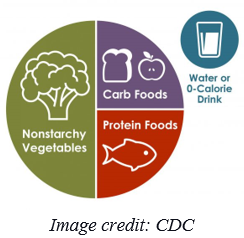
1. The plate method
The plate method tells you the amount of food in each group that you should eat during lunch and dinner. So, if you have a 9-inch plate (that’s the size of a typical dinner plate), half of it should be full of non-starchy vegetables.
The other half is equally divided between protein and grains or starches. Along with the meal, you can have a piece of fruit as a sweet treat and milk as a small drink.
2. Carb counting method
For people living with type 1 diabetes, counting carbs is a fantastic way to keep blood sugar steady. Essentially, you track your carb intake for each meal, so your glucose doesn’t oscillate beyond the required range.
It also helps you decide how much insulin you need to take. The best approach to carb counting is to sit down with your healthcare provider to work out what food items you can eat and what should be the serving size.
Beyond willpower: eating healthy with diabetes
More young people are living with diabetes than ever before. Globally, it is on an estimated 3% rise annually in adults as well as in the paediatric population. In India, the onset of type 2 diabetes is nearly two decades earlier than in the west, with a prevalence of 8 to 10%
Yet, that does not mean that you can’t live a long, healthy, and quality life. With the right nutrition plan, managing diabetes becomes easier. But a lot of it depends on your willpower to manfully resist the temptation to eat restricted items.
So, we bid you adieu with a simple trick to eat healthy: manage your environment. Don’t bring food that you’re not allowed to eat at home. Never go hungry for long periods. Make food at home so you can control calories.
